Business
How a Pellet Mill Machine Works: Step-by-Step Process Explained
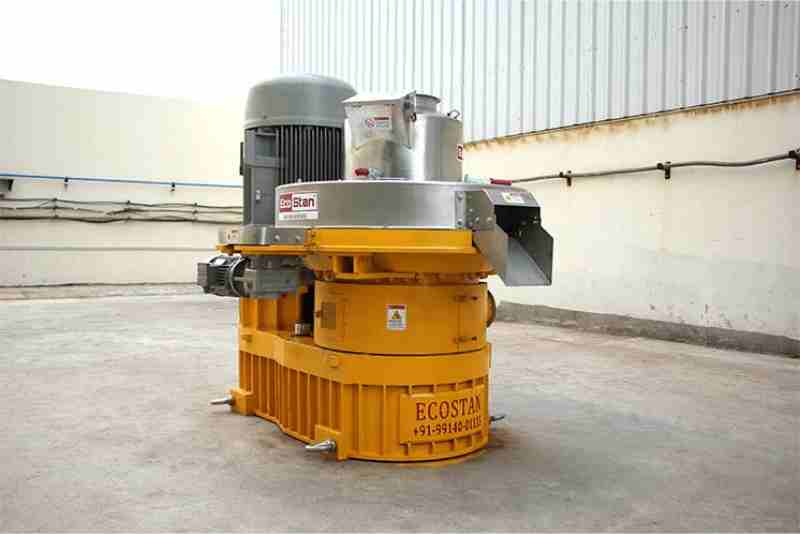

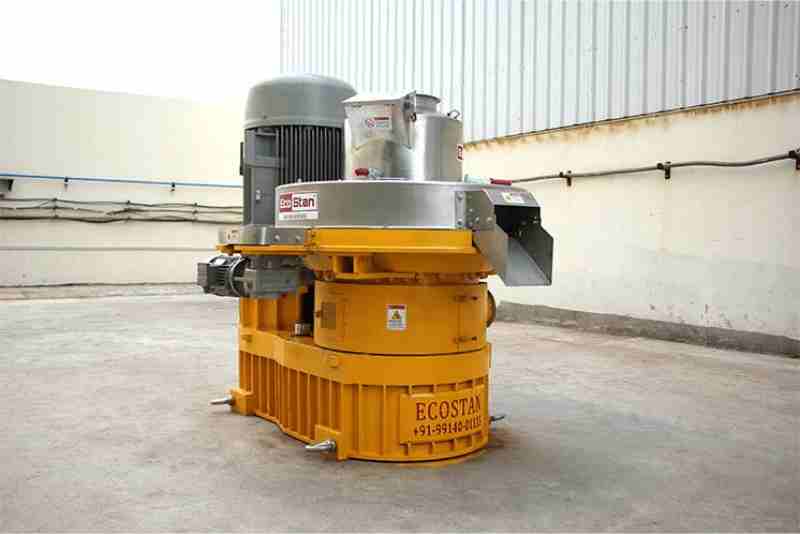
The growing demand for renewable energy and efficient biomass utilization has made pellet production an essential part of modern industrial and agricultural operations. At the heart of this process lies the Pellet Mill Machine, a powerful system designed to convert raw biomass into compact, high-density pellets. These pellets are widely used as fuel, animal feed, and raw material for various industries.
Understanding how a Pellet Mill Machine works helps businesses optimize production, improve pellet quality, and reduce operational costs. In this article, we break down the complete step-by-step working process of a Pellet Mill Machine in a clear and practical way.
What Is a Pellet Mill Machine?
A Pellet Mill Machine is a mechanical device that compresses biomass material into uniform pellets using pressure, heat, and a die-and-roller mechanism. Common raw materials include sawdust, rice husk, straw, wood chips, agricultural waste, and other biomass residues.
Pellets produced by a Pellet Mill Machine are easy to store, transport, and burn efficiently, making them a preferred alternative to loose biomass.
Step-by-Step Working Process of a Pellet Mill Machine
Step 1: Raw Material Collection and Selection
The first step in pellet production is collecting suitable raw materials. Biomass should be clean, free from stones, metals, or other impurities, and appropriate for pelletizing.
Common materials used in a Pellet Mill Machine include:
- Sawdust and wood shavings
- Paddy straw and wheat straw
- Rice husk and groundnut shells
- Corn cobs and bagasse
The quality of raw material directly affects pellet durability and calorific value.
Step 2: Size Reduction (Grinding)
Before entering the Pellet Mill Machine, raw material must be reduced to a uniform size. This is usually done using a hammer mill or grinder.
- Ideal particle size: 3–5 mm
- Ensures smooth pellet formation
- Improves compression efficiency inside the die
Uniform grinding helps the Pellet Mill Machine produce consistent pellets with fewer cracks.
Step 3: Drying the Raw Material
Moisture content plays a critical role in pellet quality. Most Pellet Mill Machines require raw material moisture between 10% and 15%.
- High moisture → soft or broken pellets
- Low moisture → poor binding and excess dust
Dryers such as rotary dryers or flash dryers are commonly used to bring the material to the correct moisture level before pelletizing.
Step 4: Conditioning and Feeding
Once dried, the material is fed into the Pellet Mill Machine through a feeder. In some setups, conditioning is done before pellet formation.
- Heat generated by friction softens lignin in biomass
- Natural lignin acts as a binder
- No chemicals are usually required
This step improves pellet strength and surface finish.
Step 5: Pelletizing Process (Core Working Principle)
This is the most important stage where the Pellet Mill Machine performs its primary function.
How it works:
- Material enters the pellet chamber
- Rollers press the material against a rotating ring die
- High pressure forces material through die holes
- Cylindrical pellets are formed as material exits the die
The combination of pressure, temperature, and mechanical force ensures dense and durable pellets.
Step 6: Cutting and Pellet Length Control
As pellets come out of the die, knives cut them into uniform lengths.
- Pellet length can be adjusted
- Ensures consistent appearance
- Improves handling and packaging
This step gives pellets their final shape.
Step 7: Cooling the Pellets
Fresh pellets are hot and soft. Cooling is essential to harden them and improve durability.
- Pellets are passed through a pellet cooler
- Temperature and moisture are reduced
- Pellets gain mechanical strength
Cooling prevents deformation during storage and transport.
Step 8: Screening and Removal of Fines
After cooling, pellets are screened to remove dust and broken particles.
- Fine particles are separated
- Recycled back into the Pellet Mill Machine
- Ensures high-quality final output
This step improves customer satisfaction and pellet efficiency.
Step 9: Packaging and Storage
The final pellets are ready for packaging or bulk storage.
- Packed in bags or stored in silos
- Easy to transport
- Long shelf life due to low moisture
Proper storage maintains pellet quality and prevents moisture absorption.
Key Advantages of Using a Pellet Mill Machine
- Efficient biomass utilization
- Reduced waste and storage space
- Uniform fuel quality
- Environment-friendly energy solution
- High output with low operating cost
A Pellet Mill Machine transforms low-value waste into a profitable and sustainable product.
Applications of Pellet Mill Machine Pellets
Pellets produced using a Pellet Mill Machine are widely used in:
- Biomass power plants
- Industrial boilers
- Residential heating systems
- Animal feed production
- Export markets
Their versatility makes pellet production a growing industry worldwide.
Conclusion:
Understanding how a Pellet Mill Machine works helps industries achieve better efficiency, consistent pellet quality, and long-term profitability. From raw material preparation to final packaging, each step plays a vital role in successful pellet production.
Ecostan Machines is a trusted name in biomass machinery manufacturing, known for delivering robust, high-performance Pellet Mill Machines tailored to diverse industrial needs. With a strong focus on innovation, durability, and customer satisfaction, Ecostan Machines provides complete pelletizing solutions that help businesses turn biomass waste into valuable energy resources.
Source:
Click for the: Full Story
You might like












 Close Menu
Close Menu